BIO-FERTILISER
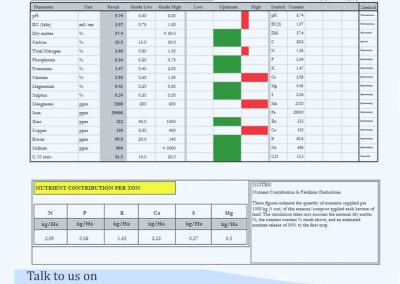
The “True Cross-flow” design of the Flexi system ensures the “waste” is retained until the fermentation process is completed and all the micro elements have been released. As the micro elements – now in dissolved form, are not removed from this process, the resultant BIO-FERTILISER is a rich organic fertilizer with a high market value.
BENEFITS of Organic fertilizer
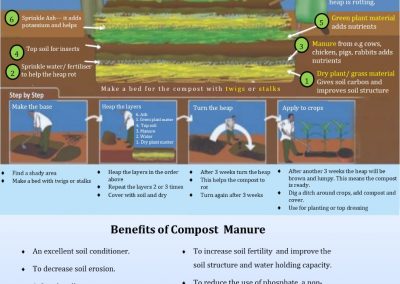
In developing countries, fertilizer is one of the most expensive input in crop production. Bio fertilizer can be used to build healthy fertile soil for crop production.
The bio fertilizer from the flexi biogas system comes out in liquid form and is highly nutritious and ready for absorption by plants without ”burning the plants”.
Diluted 1:5 or 1:10, Bio-Slurry can be applied as a top dressing or sprayed as a folia feed. Sprayed on crops, it has also proven extremely effective to be an insect and pest repellent.
Bio-fertilizer increases cereal crop productions by 10 to 30%
compared to ordinary manure. Regarding increased yields, the most responsive crops to bio-fertilizer are such as vegetables, root crops, potatoes, fruit trees, maize, and rice.
Furthermore, bio-fertilizer has the potential not only to improve soil fertility and soil structure, but also seeds treated with bio-fertilizer have given better germination rates.
Bio-fertilizer has many positive effects in addition to being a great source of nutrients, and it can be used for the following
applications;-
- As a basal manure and as a foliar application or spray, or together with irrigation water.
- As an insect repellent.
- To increase soil fertility and improve the soil structure and water holding capacity.
- To decrease soil erosion.
- To treat seeds for higher germination, disease resistance, better yields, improved coloration of fruits and vegetables, and tenderness and taste of leafy vegetables.
- To increase the feed value of fodder with low protein content.
- For concentrated feed for cattle, pigs, and fish, and the production of earth worms and algae.
- For the production of vitamin B12 and amino acids for animal growth. In addition, it contains enzymes which stimulate hunger for more food intake and better nourishment of animals.
- As a means of increasing quality and quantity of organic grown flowers and vegetables.
- To increase the availability of nutrients for soil micro-flora like nitrogen fixing and phosphor solubilising organisms.
- To reduce the use of phosphate, a non-renewable source which is being depleted globally.
- To reduce wastewater, water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions and noxious odours.
- To reduce weed growth and to diminish attractiveness to insects or flies.